
Battle of the structures.
Figure 1 shows a spoiklin class diagram of a well-structured package.
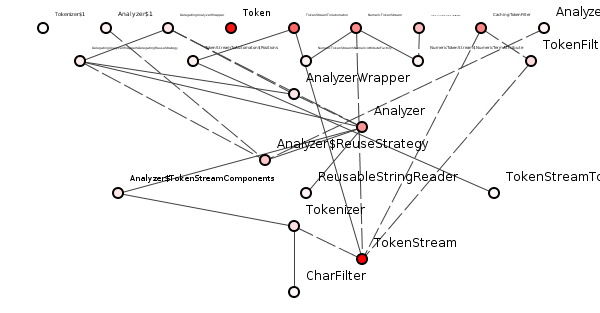
Figure 1: A good package structure from Lucene.
It is well-structured because it makes dependency-tracing relatively easy. If we choose a class randomly - say ReusableStringReader - we can easily spot dependencies on that class and hence estimate the potential cost of changes made to that class, see figure 2.
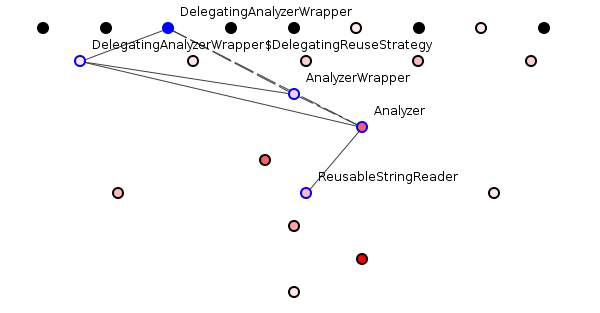
Figure 2: Tracing dependencies on ReusableStringReader.
Dependencies, however, come in two flavors. Syntactic dependencies do not rely on the meanings of the names of the connected nodes. Semantic dependencies, however, do. Are the dependencies of figure 2 also good semantic dependencies?
To answer this question, we must inspect the names of the dependent classes and ask whether they, "Make sense," in that a connection between those names might be expected within their respective epistemological domains.
So, we have an Analyzer dependent on ReusableStringReader. This makes sense; if you were building functionality to analyze something, you might well want to read strings and a, "Reusable," string reader sounds like a specific type of string reader so this semantic dependency hardly surprises. Similarly, the AnalyzerWrapper might well depend on an Analyzer. Repeating the exercise reveals a sound semantic structure.
Structure being a set of nodes and their interconnections, which, then, is more important: syntactic or semantic structure?
Let us change figure 2 to deliberately degrade its semantic structure.
A purely syntactic change involves changing the dependencies between nodes. A purely semantic change involves changing the names of nodes (adding or removing a node is both a syntactic and semantic change). So let us make the smallest semantic modification by changing ReusableStringReader's name to Banana.
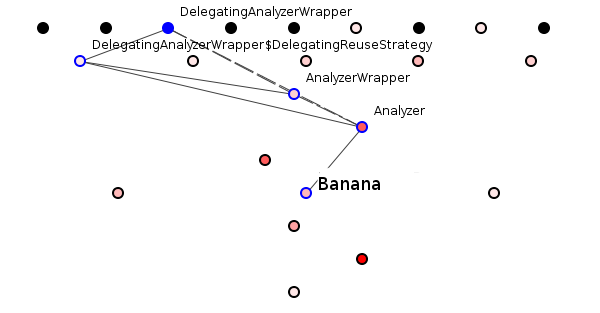
Figure 3: A semantic slip-up.
"Banana," is a ghastly name for the ReusableStringReader class. The programmer trying to understand this package would weep when seeing that the analysis functionality depends on a fruit (or herb, or whatever the hell a banana is). Monkeys depend on bananas, not analysis functionalities. This is bad semantic structure.
But if we change the code in Banana, can we still predict potential ripple effects? Yes we can, because ripple effects travel over syntactic rather than semantic dependencies. Even if we remove all semantic information - see figure 4 - we can trace potentially impacted classes.
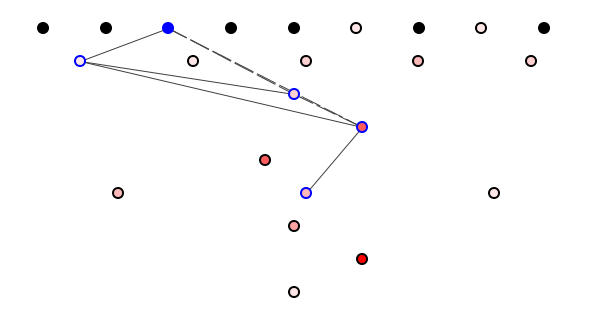
Figure 4: A semantics-free diagram.
Alternately, we can examine a badly syntactically structured package and improve its semantics to gauge the overall benefit. Figure 5 shows such bad package.
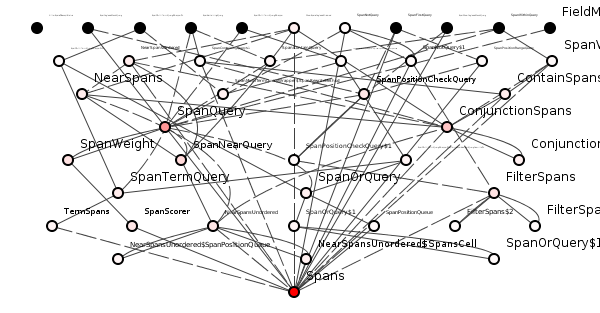
Figure 5: A dreadful package from Lucene.
Except we shall not attempt a semantic improvement.
Because even if Wittgenstein and Chomsky themselves pair-programmed figure 5 into the most well-named package in the history of software engineering, estimating change costs would still be a nightmare.
Summary
The primary purpose of good software structure is to aid impact cost estimation and, indirectly, to lower actual impact costs. Semantics are a crucial comprehension aid, but semantic soundness draped on a poor syntactic structure will cost more to update than a semantic fruit-basket supported by excellent syntactic structure.
Syntactics bitch-slap semantics.
Hard.